فوائد زيت الزيتون السوري
سيرجيلا
زيت زيتون سيرجيلا
زيت الزيتون هو أحد أنواع الدهون السائلة المستخلصة من ثمرة الزيتون. ويستخدم على نحو واسع لطهي وقلي الأطعمة وفي السلطات المتنوعة، إضافة إلى استعماله كمكون رئيسي في العديد من الصناعات مثل مستحضرات التجميل والصابون وغيرهم.
يمتاز زيت زيتون سيرجيلا بجودته العالية، فقد تم إنتاجه من أجود أنوع الزيتون في سوريا التي اشتهرت على مر الزمان بطبيعتها الخضراء ومناخها المعتدل وتربتها الخصبة وإنتاجها لأفضل أصناف الزيتون جودة في العالم.
فوائد زيت الزيتون السوري

تغذية البشرة والشعر والأظافر
يتسم زيت الزيتون بخواصه الصحية والعلاجية الكثيرة، سواء عند تناوله أو دهنه على الجسم. فهو غني بفيتامينات A وD وK وE التي تساعد على تغذية وترطيب البشرة وزيادة كثافة الشعر ولمعانه وتقوية الأظافر والعظام، إضافة إلى منع تشكّل الجذور الحرة التي تسبب الشيخوخة وظهور التجاعيد.
تقوية جهاز المناعة
يعمل زيت الزيتون على تعزيز مناعة الجسم والتصدي لأنواع مختلفة من الفيروسات والأمراض. فهو يحتوي على مضادات الأكسدة الضرورية لحماية الجسم من العدوى. كما تشمل تركيبته أحماضاً دهنية تساعد على منع التعرض إلى بعض الأمراض المناعية بما يشمل الإنتاج المفرط لخلايا الدم البيضاء.
المساهمة في فقدان الوزن
يعمل زيت الزيتون على إنقاص الوزن خاصة عند تناوله على معدة فارغة، فهو يساعد على إضفاء الإحساس بالشبع لفترة طويلة، ما يدفعك لتناول كمية أقل من الطعام والسعرات الحرارية.
تغذية البشرة والشعر والأظافر
يتسم زيت الزيتون بخواصه الصحية والعلاجية الكثيرة، سواء عند تناوله أو دهنه على الجسم. فهو غني بفيتامينات A وD وK وE التي تساعد على تغذية وترطيب البشرة وزيادة كثافة الشعر ولمعانه وتقوية الأظافر والعظام، إضافة إلى منع تشكّل الجذور الحرة التي تسبب الشيخوخة وظهور التجاعيد.
تقوية جهاز المناعة
يعمل زيت الزيتون على تعزيز مناعة الجسم والتصدي لأنواع مختلفة من الفيروسات والأمراض. فهو يحتوي على مضادات الأكسدة الضرورية لحماية الجسم من العدوى. كما تشمل تركيبته أحماضاً دهنية تساعد على منع التعرض إلى بعض الأمراض المناعية بما يشمل الإنتاج المفرط لخلايا الدم البيضاء.
المساهمة في فقدان الوزن
يعمل زيت الزيتون على إنقاص الوزن خاصة عند تناوله على معدة فارغة، فهو يساعد على إضفاء الإحساس بالشبع لفترة طويلة، ما يدفعك لتناول كمية أقل من الطعام والسعرات الحرارية.
تخليص الكبد من السموم
يسهم زيت الزيتون في تفتيت حصوات المرارة وطرح السموم من الكبد لضمان قيام الجسم بدوره على أكمل وجه.
تعزيز صحة القولون
تلعب العناصر الغذائية الموجودة في زيت الزيتون دوراً مهماً في الحفاظ على صحة القولون ونشاطه، فهي تمنع تضررخلايا القولون وتقلل من أخطار الإصابة بالسرطان.
الحماية من أمراض القلب المختلفة
أظهرت الأبحاث العملية على أن زيت الزيتون يحد من التعرض لأمراض القلب بنسبة 15%.

تخليص الكبد من السموم
يسهم زيت الزيتون في تفتيت حصوات المرارة وطرح السموم من الكبد لضمان قيام الجسم بدوره على أكمل وجه.
تعزيز صحة القولون
تلعب العناصر الغذائية الموجودة في زيت الزيتون دوراً مهماً في الحفاظ على صحة القولون ونشاطه، فهي تمنع تضررخلايا القولون وتقلل من أخطار الإصابة بالسرطان.
الحماية من أمراض القلب المختلفة
أظهرت الأبحاث العملية على أن زيت الزيتون يحد من التعرض لأمراض القلب بنسبة 15%.

تخفيض مستوى الكوليسترول في الدم
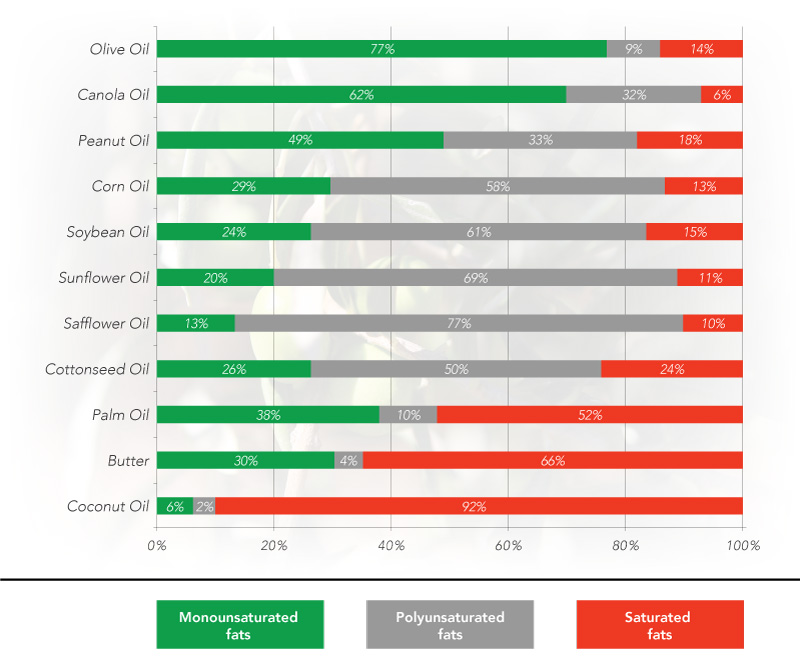
يعمل زيت الزيتون على تخفيض مستوى الكوليسترول الضار ورفع مستوى الكوليسترول الحميد في الجسم، ما يساعد على حماية القلب والشرايين من الجلطات والأمراض المزمنة، إضافة إلى زيادة إفراز الأنسولين وتعزيزه وتخفيض مستوى السكر في الدم. وتعتبر الدهون من العناصر الغذائية الأساسية، لكنها تختلف عن بعضها البعض من ناحية نفعها وضررها، إذ تمثل الدهون الأحادية غير المشبعة ما يزيد عن 75% من هذه الدهون، لذلك يعتبر زيت الزيتون الأفضل لصحة الإنسان. ويوجد نوعان من الكوليسترول، يطلق على النوع الأول اسم البروتينات الدهنية منخفضة الكثافة (LDL) أو الكوليسترول الضار لأنه يترسب على الأنسجة والشرايين ويتلف جدران الأوعية الدموية، أما النوع الثاني فيطلق عليه اسم البروتينات الدهنية عالية الكثافة (HDL)، أو الكوليسترول الحميد لأنه يزيل الكوليسترول الضار من الخلايا وينقله إلى الكبد ليتم التخلص منه.
تخفيض مستوى الكوليسترول في الدم
يعمل زيت الزيتون على تخفيض مستوى الكوليسترول الضار ورفع مستوى الكوليسترول الحميد في الجسم، ما يساعد على حماية القلب والشرايين من الجلطات والأمراض المزمنة، إضافة إلى زيادة إفراز الأنسولين وتعزيزه وتخفيض مستوى السكر في الدم. وتعتبر الدهون من العناصر الغذائية الأساسية، لكنها تختلف عن بعضها البعض من ناحية نفعها وضررها، إذ تمثل الدهون الأحادية غير المشبعة ما يزيد عن 75% من هذه الدهون، لذلك يعتبر زيت الزيتون الأفضل لصحة الإنسان. ويوجد نوعان من الكوليسترول، يطلق على النوع الأول اسم البروتينات الدهنية منخفضة الكثافة (LDL) أو الكوليسترول الضار لأنه يترسب على الأنسجة والشرايين ويتلف جدران الأوعية الدموية، أما النوع الثاني فيطلق عليه اسم البروتينات الدهنية عالية الكثافة (HDL)، أو الكوليسترول الحميد لأنه يزيل الكوليسترول الضار من الخلايا وينقله إلى الكبد ليتم التخلص منه.
أنواع الدهون
الدهون الأحادية غير المشبعة:
تتسم هذه الدهون بقوامها السائل في ظروف الحرارة المعتدلة. وتعمل على تنظيم مستويات الكوليسترول في الدم من خلال تخفيض الكوليسترول الضارLDL وزيادة مستوى الكوليسترول الحميد HDL، علاوة على التقليل من خطر الإصابة بأمراض القلب والأوعية الدموية.
الدهون غير المشبعة:
وهي دهون سائلة، تحافظ على قوامها في ظروف الحرارة المعتدلة وتساعد على تخفيض مستويات الكوليسترول الحميد والضار في الدم. وتعتبر أقل استقراراً في الطهي من الدهون الأحادية غير المشبعة، كما تزيد من هرم الخلايا.
الدهون المشبعة:
تتسم هذه الدهون بقوام صلب أو شبه صلب في ظروف الحرارة المعتدلة. وتؤدي إلى زيادة مستوى الكوليسترول الضار في الدم، وبالتالي التعرض لخطر الإصابة بأمراض الشرايين التاجية.
الدهون المتحوّلة:
تعتبر من الدهون غير المشبعة التي يتم إنتاجها صناعياً عبر هدرجة الزيوت النباتية لزيادة صلابتها وعمرها الافتراضي والتقليل من حاجتها إلى التبريد. تتسم بقوام صلب في درجات الحرارة المنخفضة وتزيد من خطر الإصابة بأمراض القلب والشرايين التاجية والسرطان .